Introduction
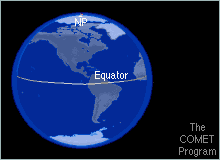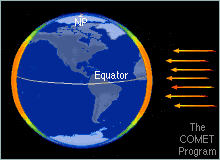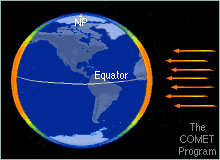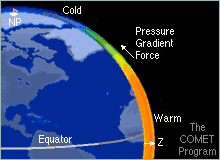
This collection of information, on tropical meteorology for aeronautical forecasters, consists of selections from the Introduction to Tropical Meteorology, 2nd Edition online textbook.
After completing this study guide you should be able to:
- Describe the characteristics of tropical climates and their role in the global system
- Describe the processes that influence the motion of the atmosphere
- Identify the contributors to the global circulation pattern and their characteristics
- Identify the characteristics of remotely-sensed observations
- Identify the sources of intraseasonal and interannual variability in the tropical atmosphere
- Determine the presence of Kelvin and n=1 Equatorial Rossby waves
- Identify ENSO's climatological impacts
- Describe the formation of tropical precipitation and factors that influence it
- Use observation tools and NWP to create a forecast
This section begins with an overview of energy balance and the global climate system. Various definitions of the tropics are presented. The role of the tropics in the global energy and momentum balance is explained. Atmospheric structure of temperature and humidity are discussed in terms of latitudinal variability. Pressure ranges and scales of atmospheric motion in the tropics are reviewed. Seasonal and geographic distribution and the diurnal cycle of surface temperature and the influencing factors are examined in detail. Finally, we review tropical air masses and climates.
The topics in this section support your development of competency in analyzing and continuously monitoring the weather situation as part of your aeronautical forecasting activities. With the challenges associated with forecasting in the Tropics, solid background knowledge of the information that follows is important as you develop your mental model of the weather situation as part of your daily forecast process.
Let's begin by defining the tropics.
EACH link will open a new tab or window, close the tab or window to return.
- Defining the Tropics
- Energy Balance
- Atmospheric Structure
- Temperature
- Moisture and Precipitation
- Momentum Balance
- Regional Influences
- References